Introduction of UNS N07041(Udimet alloy R41)
Tech Center 2025-08-19 174
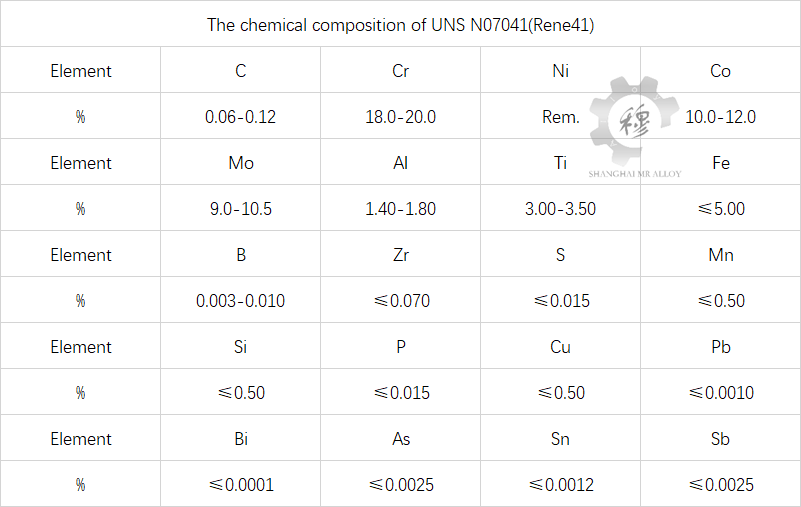
Overview of UNS N07041 (Udimet alloy R41)
UNS N07041 (Udimet alloy R41) is a precipitation-hardening nickel-based deformable superalloy. Within the range of 650-900℃, it features high tensile and creep strength, as well as excellent oxidation resistance. Due to the high content of aluminum, titanium and aluminum in the alloy, it is rather difficult to open the ingot. However, the deformed material has good plasticity and can be cold-formed in the annealed state or welded. During heat treatment, strain aging cracks are prone to occur in the welded parts. The varieties of alloys include thin plates, strips, wires, discs, rings, forgings, bars and precision castings, etc. They are suitable for manufacturing high-temperature components of aviation and aerospace engines that require high strength below 870℃ and oxidation resistance below 980℃.
Smelting and casting process of UNS N07041 (Udimet alloy R41)
The alloy is processed by vacuum induction melting, vacuum induction melting plus electroslag remelting or vacuum arc remelting.
Application Overview and Special Requirements of UNS N07041 (Udimet alloy R41)
This alloy is widely used in the manufacture of high-temperature load-bearing components for aviation and aerospace engines, such as guide vanes, combustion chambers, turbines, high-temperature load-bearing parts of guide vanes, shafts, discs, blades and fasteners, etc. Strain aging cracks in sheet metal welded parts during heat treatment can be addressed by over-aging treatment before welding or by controlling the cooling rate after solution treatment before welding, followed by standard heat treatment after welding.
Soldering performance of UNS N07041 (Udimet alloy R41)
Alloys can be welded by fusion welding, diffusion welding, brazing and friction welding. Fusion welding can be carried out either by electron beam welding or by argon arc welding. There is a tendency for strain aging cracks to occur in the fusion weld seam during heat treatment. To minimize this tendency, slow solution annealing at 1080℃ should be carried out before welding, followed by cooling at 22℃/min to 650℃. Another approach is to carry out aging treatment before welding, that is, to 1080℃ for 30 minutes, cool to 980℃ at a rate of 1.7-4.4℃/min for 4 hours, cool to 870℃ at a rate of 1.7-4.4℃/min for 4 hours, then cool to 760℃ at a rate of 1.7-4.4℃/min for 16 hours, and air cool. After welding, when eliminating welding stress and restoring performance, rapid heating should be carried out through the aging hardening temperature range, which can eliminate the tendency of strain aging cracking. The use of fine-grained and low-impurity content base materials eliminates mechanical work hardening, and the low welding line energy can also reduce the tendency of strain aging cracking.
Heat treatment process for UNS N07041 (Udimet alloy R41) parts
(1) When working at a lower temperature and requiring parts to have high tensile strength and fatigue performance, it is recommended to use 1080℃ air cooling +760℃ for 16 hours, air cooling.
(2) When working at high temperatures and the material is required to have high thermal strength, the appropriate heat treatment specification is 1180℃ air cooling +900℃ for 4 hours, air cooling.
(3) For components such as ring-shaped parts that require welding, it is recommended to use 1120℃ for 30 minutes with air cooling followed by 900 ℃ for 4 hours with air cooling.
The above is all about UNS N07041 (Udimet alloy R41) nickel-based deformable superalloy. Our company’s official website (wellalloy.com) updates alloy-related information daily. We welcome everyone’s suggestions and exchanges.
