Introduction of Inconel N06230(W.Nr.2.4733、Haynes230)
Tech Center 2025-08-13 159
Introduction to Inconel N06230(Haynes230)
Inconel N06230(Haynes230) alloy is a nickel-based superalloy strengthened by solid solution with W and Mo elements and by carbides as the second phase. This solid solution strengthened nickel-based alloy is derived from the Ni-Cr-Mo-W alloy system. The Ni element in the alloy provides a stable austenitic matrix and enhances the high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance of the alloy by adding Cr, Mo, W, C, and B. Effective solid solution strengthening is achieved by increasing the content of W element. The formation of Cr-rich M23C6 carbides is promoted by adding C, and the precipitation of M23C6 carbides at the austenite matrix and annealing twin boundaries is used to nail dislocations, thereby enhancing the creep strength of the alloy. La is added to the alloy to improve its oxidation resistance, and B is used for grain boundary strengthening. Make the alloy have good strength, thermal stability and corrosion resistance. This alloy has a small coefficient of expansion, resulting in low thermal stress in components. It is easy to process and weld, and its long-term service temperature in an oxidizing atmosphere can reach 1150℃
The working temperature of the combustion chamber of aerospace engines can reach above 1100 ℃. The combustion chamber materials are required to have good high-temperature strength, oxidation resistance, and microstructure thermal stability. Inconel N06230(Haynes230) alloy is used in key parts such as the flange of the engine combustion chamber. This alloy has the following breakthroughs and improvements compared with traditional combustion chamber alloys: It replaces the single strengthening of W element with the composite strengthening of W and Mo elements, enhancing the solid solution strengthening effect; The high-temperature creep resistance and high-temperature oxidation resistance of the alloy were enhanced through microalloying with La element. A large amount of M6C carbides in the alloy have good thermal stability in the Ni matrix, which not only plays a role in high-temperature strengthening but also improves the thermal stability of the alloy structure.
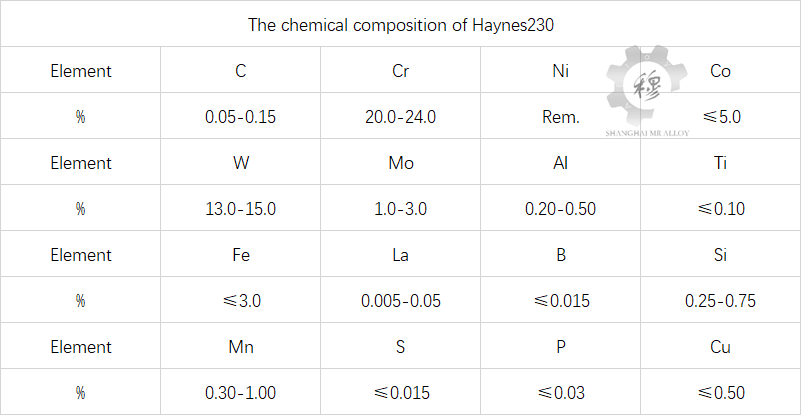
Inconel N06230(Haynes230) alloy is a nickel-based superalloy strengthened by solid solution with W and Mo elements and by carbides as the second phase. This solid solution strengthened nickel-based alloy is derived from the Ni-Cr-Mo-W alloy system. The main alloying elements added to the alloy are Cr, Mo, W, C, B, etc., in order to enhance the high-temperature mechanical properties and oxidation resistance of the alloy. The Cr element mainly plays a role in solid solution strengthening and is also a carbide-forming element. On the one hand, Cr can dissolve in the matrix phase to strengthen the structure; on the other hand, it can combine with carbon to form M23C6 type compounds, which to a certain extent play a role in precipitation strengthening and grain boundary strengthening. When the Cr content is between 14% and 20%, an increase in Cr content has little effect on the strength of the matrix. However, when the Cr content exceeds 20%, Cr will lower the solution temperature of the γ “phase, thereby also reducing the high-temperature strength of the alloy. Co is beneficial for enhancing the thermal strength of nickel-based alloys within the high-temperature range and is also helpful in resisting high-temperature thermal corrosion. Co in Ni-Cr solid solutions can reduce the stacking fault energy and play a good solid solution strengthening role. The increase of Co content in the alloy is beneficial to the microstructure stability and creep performance of the alloy. When the Co content is less than 10%, the high-temperature strength decreases. W is the main strengthening element in the γ matrix. The atomic radius of W is larger than that of the matrix Ni, and the solid solution strengthening effect is very obvious. La element is an effective trace active element in superalloys, and it usually shows obvious segregation at the grain boundaries, phase interfaces and surfaces of the alloy. The La element can enhance the high-temperature oxidation resistance and corrosion resistance of alloys by improving the viscosity and chemical composition of the oxide film. Solution treatment is one of the most important heat treatment methods for superalloys, and its main purposes are threefold
1) It is to dissolve carbides, γ’, etc. within the matrix to obtain a uniform solid solution;
2) It is to obtain an appropriate grain size to ensure high-temperature creep resistance and endurance performance;
3) It is to reduce or eliminate the segregation of alloying elements and make the chemical composition in the alloy matrix uniform.
Solution treatment can reduce the segregation of alloys, make the structure uniform, and refine the γ’ phase, promoting the precipitation of fine γ’ phases. Relevant studies have shown that after solution treatment of Inconel N06230(Haynes230) alloy, the creep life at 927 MPa / 62 ℃ gradually increases with the increase of solution temperature, while the creep elongation at break changes little. However, the selection of solution treatment temperature has a significant impact on the grain size of the alloy, as austenitic alloys have an abnormal growth temperature range. That is, if solution treatment is carried out beyond a certain critical temperature, the matrix grains will abnormally grow. Aging treatment is generally carried out after solution treatment and intermediate treatment, and can also be done after direct solution treatment. The purpose of aging treatment is to further precipitate fine γ’ phases in the matrix, forming a dispersion strengthening effect, thereby enhancing the mechanical properties of the alloy.

